Chief Sustainability Officers
Overview
Salary
Demand
Core Tasks
Technology Skills
Tools Used
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Top 10 Skills
Top 10 Abilities
Top 10 Work Activities
Detailed Work Activities
Work Context
Education
Majors
Interests
Top 10 Work Styles
Work Values
Overview
Job Zone Five: Extensive Preparation Needed
Experience
Extensive skill, knowledge, and experience are needed for these occupations. Many require more than five years of experience. For example, surgeons must complete four years of college and an additional five to seven years of specialized medical training to be able to do their job.
Education
Most of these occupations require graduate school. For example, they may require a master's degree, and some require a Ph.D., M.D., or J.D. (law degree).
Job Training
Employees may need some on-the-job training, but most of these occupations assume that the person will already have the required skills, knowledge, work-related experience, and/or training.
Examples
These occupations often involve coordinating, training, supervising, or managing the activities of others to accomplish goals. Very advanced communication and organizational skills are required. Examples include pharmacists, lawyers, astronomers, biologists, clergy, neurologists, and veterinarians.
Communicate and coordinate with management, shareholders, customers, and employees to address sustainability issues. Enact or oversee a corporate sustainability strategy.
Salary Salary
Salary at 10th Percentile: $62K
Salary at 25th Percentile: $114K
Median Salary: $185K
Salary at 75th Percentile: $208K
Salary at 90th Percentile: $208K
Demand
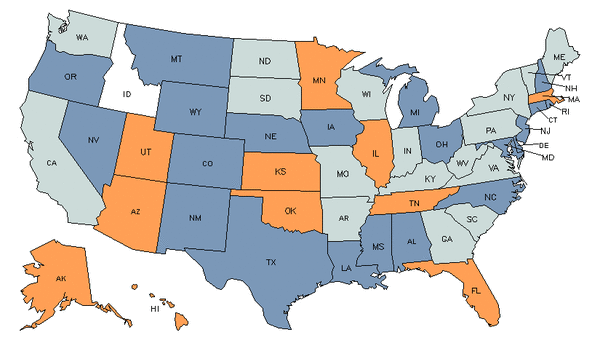

Core Tasks
Develop or execute strategies to address issues such as energy use, resource conservation, recycling, pollution reduction, waste elimination, transportation, education, and building design.
Monitor and evaluate effectiveness of sustainability programs.
Develop, or oversee the development of, sustainability evaluation or monitoring systems.
Supervise employees or volunteers working on sustainability projects.
Develop sustainability reports, presentations, or proposals for supplier, employee, academia, media, government, public interest, or other groups.
Develop, or oversee the development of, marketing or outreach media for sustainability projects or events.
Identify and evaluate pilot projects or programs to enhance the sustainability research agenda.
Create and maintain sustainability program documents, such as schedules and budgets.
Formulate or implement sustainability campaign or marketing strategies.
Research environmental sustainability issues, concerns, or stakeholder interests.
Direct sustainability program operations to ensure compliance with environmental or governmental regulations.
Develop methodologies to assess the viability or success of sustainability initiatives.
Evaluate and approve proposals for sustainability projects, considering factors such as cost effectiveness, technical feasibility, and integration with other initiatives.
Review sustainability program objectives, progress, or status to ensure compliance with policies, standards, regulations, or laws.
Write and distribute financial or environmental impact reports.
Write project proposals, grant applications, or other documents to pursue funding for environmental initiatives.
Identify educational, training, or other development opportunities for sustainability employees or volunteers.
Conduct risk assessments related to sustainability and the environment.
Technology Skills
Technology
Example
Hot Technology
Tools Used
Tool
Example
Top 10 Knowledge Required
English Language
86%
Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, rules of composition, and grammar.
Administration and Management
83%
Knowledge of business and management principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people and resources.
Law and Government
74%
Knowledge of laws, legal codes, court procedures, precedents, government regulations, executive orders, agency rules, and the democratic political process.
Communications and Media
72%
Knowledge of media production, communication, and dissemination techniques and methods. This includes alternative ways to inform and entertain via written, oral, and visual media.
Building and Construction
70%
Knowledge of materials, methods, and the tools involved in the construction or repair of houses, buildings, or other structures such as highways and roads.
Customer and Personal Service
69%
Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Education and Training
69%
Knowledge of principles and methods for curriculum and training design, teaching and instruction for individuals and groups, and the measurement of training effects.
Economics and Accounting
64%
Knowledge of economic and accounting principles and practices, the financial markets, banking and the analysis and reporting of financial data.
Sales and Marketing
63%
Knowledge of principles and methods for showing, promoting, and selling products or services. This includes marketing strategy and tactics, product demonstration, sales techniques, and sales control systems.
Transportation
63%
Knowledge of principles and methods for moving people or goods by air, rail, sea, or road, including the relative costs and benefits.
Top 10 Skills
Critical Thinking
83%
Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Writing
83%
Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Active Listening
80%
Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Complex Problem Solving
80%
Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Reading Comprehension
80%
Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Speaking
80%
Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Judgment and Decision Making
78%
Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Persuasion
78%
Persuading others to change their minds or behavior.
Social Perceptiveness
78%
Being aware of others' reactions and understanding why they react as they do.
Systems Analysis
78%
Determining how a system should work and how changes in conditions, operations, and the environment will affect outcomes.
Top 10 Abilities
Written Expression
83%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in writing so others will understand.
Oral Comprehension
80%
The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
Oral Expression
80%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
Speech Clarity
80%
The ability to speak clearly so others can understand you.
Speech Recognition
80%
The ability to identify and understand the speech of another person.
Written Comprehension
80%
The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
Deductive Reasoning
78%
The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
Fluency of Ideas
78%
The ability to come up with a number of ideas about a topic (the number of ideas is important, not their quality, correctness, or creativity).
Inductive Reasoning
78%
The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events).
Originality
78%
The ability to come up with unusual or clever ideas about a given topic or situation, or to develop creative ways to solve a problem.
Top 10 Work Activities
Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates
97%
Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person.
Getting Information
96%
Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
Establishing and Maintaining Interpersonal Relationships
94%
Developing constructive and cooperative working relationships with others, and maintaining them over time.
Making Decisions and Solving Problems
93%
Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
Communicating with Persons Outside Organization
90%
Communicating with people outside the organization, representing the organization to customers, the public, government, and other external sources. This information can be exchanged in person, in writing, or by telephone or e-mail.
Developing Objectives and Strategies
90%
Establishing long-range objectives and specifying the strategies and actions to achieve them.
Interpreting the Meaning of Information for Others
89%
Translating or explaining what information means and how it can be used.
Organizing, Planning, and Prioritizing Work
88%
Developing specific goals and plans to prioritize, organize, and accomplish your work.
Thinking Creatively
87%
Developing, designing, or creating new applications, ideas, relationships, systems, or products, including artistic contributions.
Updating and Using Relevant Knowledge
86%
Keeping up-to-date technically and applying new knowledge to your job.
Detailed Work Activities
Evaluate program effectiveness.
Implement organizational process or policy changes.
Develop sustainable organizational policies or practices.
Manage control system activities in organizations.
Supervise workers performing environmentally sustainable activities.
Prepare operational progress or status reports.
Present sustainable products or services information to the public.
Develop marketing plans or strategies for environmental initiatives.
Manage outreach activities.
Identify opportunities for green initiatives.
Schedule activities or facility use.
Maintain operational records for green energy processes or other environmentally-sustainable activities.
Identify environmental concerns.
Direct organizational operations, projects, or services.
Analyze data to determine project feasibility.
Evaluate environmental or sustainability projects.
Develop procedures to evaluate organizational activities.
Evaluate green operations or programs for compliance with standards or regulations.
Prepare financial documents, reports, or budgets.
Prepare proposals or grant applications to obtain project funding.
Work Context
Electronic Mail
How often do you use electronic mail in this job?
Indoors, Environmentally Controlled
How often does this job require working indoors in environmentally controlled conditions?
Telephone
How often do you have telephone conversations in this job?
Work With Work Group or Team
How important is it to work with others in a group or team in this job?
Face-to-Face Discussions
How often do you have to have face-to-face discussions with individuals or teams in this job?
Contact With Others
How much does this job require the worker to be in contact with others (face-to-face, by telephone, or otherwise) in order to perform it?
Structured versus Unstructured Work
To what extent is this job structured for the worker, rather than allowing the worker to determine tasks, priorities, and goals?
Freedom to Make Decisions
How much decision making freedom, without supervision, does the job offer?
Coordinate or Lead Others
How important is it to coordinate or lead others in accomplishing work activities in this job?
Deal With External Customers
How important is it to work with external customers or the public in this job?
Education
Majors based on the broader career Chief Executives
Major
Interests
Enterprising
100%
Enterprising occupations frequently involve starting up and carrying out projects. These occupations can involve leading people and making many decisions. Sometimes they require risk taking and often deal with business.
Conventional
62%
Conventional occupations frequently involve following set procedures and routines. These occupations can include working with data and details more than with ideas. Usually there is a clear line of authority to follow.
Investigative
62%
Investigative occupations frequently involve working with ideas, and require an extensive amount of thinking. These occupations can involve searching for facts and figuring out problems mentally.
Artistic
39%
Artistic occupations frequently involve working with forms, designs and patterns. They often require self-expression and the work can be done without following a clear set of rules.
Social
34%
Social occupations frequently involve working with, communicating with, and teaching people. These occupations often involve helping or providing service to others.
Realistic
15%
Realistic occupations frequently involve work activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions. They often deal with plants, animals, and real-world materials like wood, tools, and machinery. Many of the occupations require working outside, and do not involve a lot of paperwork or working closely with others.
Top 10 Work Styles
Leadership
97%
Job requires a willingness to lead, take charge, and offer opinions and direction.
Initiative
95%
Job requires a willingness to take on responsibilities and challenges.
Cooperation
94%
Job requires being pleasant with others on the job and displaying a good-natured, cooperative attitude.
Persistence
93%
Job requires persistence in the face of obstacles.
Integrity
92%
Job requires being honest and ethical.
Analytical Thinking
91%
Job requires analyzing information and using logic to address work-related issues and problems.
Adaptability/Flexibility
90%
Job requires being open to change (positive or negative) and to considerable variety in the workplace.
Innovation
90%
Job requires creativity and alternative thinking to develop new ideas for and answers to work-related problems.
Independence
86%
Job requires developing one's own ways of doing things, guiding oneself with little or no supervision, and depending on oneself to get things done.
Achievement/Effort
84%
Job requires establishing and maintaining personally challenging achievement goals and exerting effort toward mastering tasks.
Work Values
Achievement
96%
Occupations that satisfy this work value are results oriented and allow employees to use their strongest abilities, giving them a feeling of accomplishment. Corresponding needs are Ability Utilization and Achievement.
Independence
96%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to work on their own and make decisions. Corresponding needs are Creativity, Responsibility and Autonomy.
Working Conditions
91%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer job security and good working conditions. Corresponding needs are Activity, Compensation, Independence, Security, Variety and Working Conditions.
Recognition
86%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer advancement, potential for leadership, and are often considered prestigious. Corresponding needs are Advancement, Authority, Recognition and Social Status.
Relationships
72%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to provide service to others and work with co-workers in a friendly non-competitive environment. Corresponding needs are Co-workers, Moral Values and Social Service.
Support
48%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer supportive management that stands behind employees. Corresponding needs are Company Policies, Supervision: Human Relations and Supervision: Technical.
