Actors
Overview
Salary
Demand
Core Tasks
Technology Skills
Tools Used
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Top 10 Skills
Top 10 Abilities
Top 10 Work Activities
Detailed Work Activities
Work Context
Education
Majors
Interests
Top 10 Work Styles
Work Values
Related Careers
Overview
Job Zone Two: Some Preparation Needed
Experience
Some previous work-related skill, knowledge, or experience is usually needed. For example, a teller would benefit from experience working directly with the public.
Education
These occupations usually require a high school diploma.
Job Training
Employees in these occupations need anywhere from a few months to one year of working with experienced employees. A recognized apprenticeship program may be associated with these occupations.
Examples
These occupations often involve using your knowledge and skills to help others. Examples include orderlies, counter and rental clerks, customer service representatives, security guards, upholsterers, and tellers.
Play parts in stage, television, radio, video, or film productions, or other settings for entertainment, information, or instruction. Interpret serious or comic role by speech, gesture, and body movement to entertain or inform audience. May dance and sing.
Hourly Salary
Hourly at 10th Percentile: $10.51
Hourly at 25th Percentile: $14.04
Median Hourly: $21.88
Hourly at 75th Percentile: $30.38
Hourly at 90th Percentile: $64.92
Demand
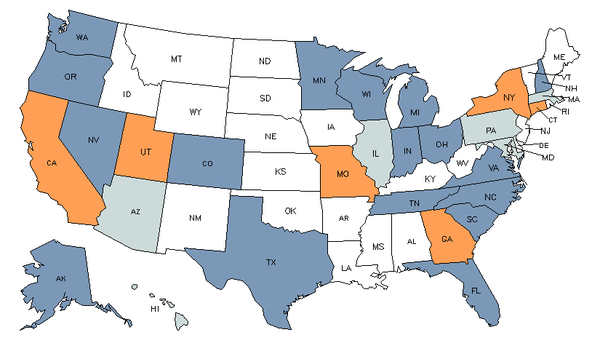

Core Tasks
Collaborate with other actors as part of an ensemble.
Portray and interpret roles, using speech, gestures, and body movements, to entertain, inform, or instruct radio, film, television, or live audiences.
Work closely with directors, other actors, and playwrights to find the interpretation most suited to the role.
Perform humorous and serious interpretations of emotions, actions, and situations, using body movements, facial expressions, and gestures.
Study and rehearse roles from scripts to interpret, learn and memorize lines, stunts, and cues as directed.
Attend auditions and casting calls to audition for roles.
Learn about characters in scripts and their relationships to each other to develop role interpretations.
Sing or dance during dramatic or comedic performances.
Tell jokes, perform comic dances, songs and skits, impersonate mannerisms and voices of others, contort face, and use other devices to amuse audiences.
Work with other crew members responsible for lighting, costumes, make-up, and props.
Read from scripts or books to narrate action or to inform or entertain audiences, utilizing few or no stage props.
Promote productions using means such as interviews about plays or movies.
Prepare and perform action stunts for motion picture, television, or stage productions.
Write original or adapted material for dramas, comedies, puppet shows, narration, or other performances.
Introduce performances and performers to stimulate excitement and coordinate smooth transition of acts during events.
Construct puppets and ventriloquist dummies, and sew accessory clothing, using hand tools and machines.
Dress in comical clown costumes and makeup, and perform comedy routines to entertain audiences.
Perform original and stock tricks of illusion to entertain and mystify audiences, occasionally including audience members as participants.
Manipulate strings, wires, rods, or fingers to animate puppets or dummies in synchronization with talking, singing, or recorded programs.
Technology Skills
Technology
Example
Hot Technology
Tools Used
Tool
Example
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Fine Arts
94%
Knowledge of the theory and techniques required to compose, produce, and perform works of music, dance, visual arts, drama, and sculpture.
English Language
87%
Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, rules of composition, and grammar.
Communications and Media
83%
Knowledge of media production, communication, and dissemination techniques and methods. This includes alternative ways to inform and entertain via written, oral, and visual media.
Sociology and Anthropology
69%
Knowledge of group behavior and dynamics, societal trends and influences, human migrations, ethnicity, cultures and their history and origins.
Psychology
66%
Knowledge of human behavior and performance; individual differences in ability, personality, and interests; learning and motivation; psychological research methods; and the assessment and treatment of behavioral and affective disorders.
Customer and Personal Service
62%
Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Sales and Marketing
58%
Knowledge of principles and methods for showing, promoting, and selling products or services. This includes marketing strategy and tactics, product demonstration, sales techniques, and sales control systems.
Education and Training
55%
Knowledge of principles and methods for curriculum and training design, teaching and instruction for individuals and groups, and the measurement of training effects.
Administration and Management
52%
Knowledge of business and management principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people and resources.
History and Archeology
52%
Knowledge of historical events and their causes, indicators, and effects on civilizations and cultures.
Top 10 Skills
Reading Comprehension
78%
Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Speaking
78%
Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Active Listening
75%
Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Social Perceptiveness
75%
Being aware of others' reactions and understanding why they react as they do.
Critical Thinking
60%
Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Monitoring
60%
Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
Time Management
60%
Managing one's own time and the time of others.
Complex Problem Solving
58%
Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Coordination
58%
Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions.
Judgment and Decision Making
58%
Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Top 10 Abilities
Oral Expression
83%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
Oral Comprehension
80%
The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
Memorization
78%
The ability to remember information such as words, numbers, pictures, and procedures.
Speech Clarity
78%
The ability to speak clearly so others can understand you.
Written Comprehension
78%
The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
Originality
75%
The ability to come up with unusual or clever ideas about a given topic or situation, or to develop creative ways to solve a problem.
Near Vision
73%
The ability to see details at close range (within a few feet of the observer).
Problem Sensitivity
63%
The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem.
Fluency of Ideas
60%
The ability to come up with a number of ideas about a topic (the number of ideas is important, not their quality, correctness, or creativity).
Selective Attention
60%
The ability to concentrate on a task over a period of time without being distracted.
Top 10 Work Activities
Establishing and Maintaining Interpersonal Relationships
92%
Developing constructive and cooperative working relationships with others, and maintaining them over time.
Thinking Creatively
89%
Developing, designing, or creating new applications, ideas, relationships, systems, or products, including artistic contributions.
Performing for or Working Directly with the Public
84%
Performing for people or dealing directly with the public. This includes serving customers in restaurants and stores, and receiving clients or guests.
Performing General Physical Activities
81%
Performing physical activities that require considerable use of your arms and legs and moving your whole body, such as climbing, lifting, balancing, walking, stooping, and handling of materials.
Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates
79%
Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person.
Communicating with Persons Outside Organization
66%
Communicating with people outside the organization, representing the organization to customers, the public, government, and other external sources. This information can be exchanged in person, in writing, or by telephone or e-mail.
Getting Information
66%
Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events
64%
Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
Handling and Moving Objects
61%
Using hands and arms in handling, installing, positioning, and moving materials, and manipulating things.
Monitor Processes, Materials, or Surroundings
60%
Monitoring and reviewing information from materials, events, or the environment, to detect or assess problems.
Detailed Work Activities
Study scripts to determine project requirements.
Practice athletic or artistic skills.
Collaborate with others to prepare or perform artistic productions.
Entertain public with comedic or dramatic performances.
Audition for roles.
Collaborate with others to determine technical details of productions.
Perform music for the public.
Promote products, activities, or organizations.
Write material for artistic or entertainment purposes.
Inform viewers, listeners, or audiences.
Construct distinctive physical objects for artistic, functional, or commercial purposes.
Work Context
Work With Work Group or Team
How important is it to work with others in a group or team in this job?
Physical Proximity
To what extent does this job require the worker to perform job tasks in close physical proximity to other people?
Electronic Mail
How often do you use electronic mail in this job?
Public Speaking
How often do you have to perform public speaking in this job?
Contact With Others
How much does this job require the worker to be in contact with others (face-to-face, by telephone, or otherwise) in order to perform it?
Time Pressure
How often does this job require the worker to meet strict deadlines?
Face-to-Face Discussions
How often do you have to have face-to-face discussions with individuals or teams in this job?
Indoors, Environmentally Controlled
How often does this job require working indoors in environmentally controlled conditions?
Level of Competition
To what extent does this job require the worker to compete or to be aware of competitive pressures?
Deal With External Customers
How important is it to work with external customers or the public in this job?
Education
Interests
Artistic
96%
Artistic occupations frequently involve working with forms, designs and patterns. They often require self-expression and the work can be done without following a clear set of rules.
Enterprising
67%
Enterprising occupations frequently involve starting up and carrying out projects. These occupations can involve leading people and making many decisions. Sometimes they require risk taking and often deal with business.
Social
43%
Social occupations frequently involve working with, communicating with, and teaching people. These occupations often involve helping or providing service to others.
Realistic
39%
Realistic occupations frequently involve work activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions. They often deal with plants, animals, and real-world materials like wood, tools, and machinery. Many of the occupations require working outside, and do not involve a lot of paperwork or working closely with others.
Conventional
24%
Conventional occupations frequently involve following set procedures and routines. These occupations can include working with data and details more than with ideas. Usually there is a clear line of authority to follow.
Investigative
19%
Investigative occupations frequently involve working with ideas, and require an extensive amount of thinking. These occupations can involve searching for facts and figuring out problems mentally.
Top 10 Work Styles
Cooperation
100%
Job requires being pleasant with others on the job and displaying a good-natured, cooperative attitude.
Initiative
97%
Job requires a willingness to take on responsibilities and challenges.
Persistence
97%
Job requires persistence in the face of obstacles.
Adaptability/Flexibility
96%
Job requires being open to change (positive or negative) and to considerable variety in the workplace.
Dependability
96%
Job requires being reliable, responsible, and dependable, and fulfilling obligations.
Social Orientation
96%
Job requires preferring to work with others rather than alone, and being personally connected with others on the job.
Achievement/Effort
95%
Job requires establishing and maintaining personally challenging achievement goals and exerting effort toward mastering tasks.
Stress Tolerance
93%
Job requires accepting criticism and dealing calmly and effectively with high stress situations.
Self Control
91%
Job requires maintaining composure, keeping emotions in check, controlling anger, and avoiding aggressive behavior, even in very difficult situations.
Concern for Others
84%
Job requires being sensitive to others' needs and feelings and being understanding and helpful on the job.
Work Values
Relationships
86%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to provide service to others and work with co-workers in a friendly non-competitive environment. Corresponding needs are Co-workers, Moral Values and Social Service.
Achievement
81%
Occupations that satisfy this work value are results oriented and allow employees to use their strongest abilities, giving them a feeling of accomplishment. Corresponding needs are Ability Utilization and Achievement.
Independence
67%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to work on their own and make decisions. Corresponding needs are Creativity, Responsibility and Autonomy.
Recognition
67%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer advancement, potential for leadership, and are often considered prestigious. Corresponding needs are Advancement, Authority, Recognition and Social Status.
Working Conditions
60%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer job security and good working conditions. Corresponding needs are Activity, Compensation, Independence, Security, Variety and Working Conditions.
Support
29%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer supportive management that stands behind employees. Corresponding needs are Company Policies, Supervision: Human Relations and Supervision: Technical.
