Careers
>Arts, Audio/Video Technology & Communications
>Performing Arts
>Media Programming Directors
Media Programming Directors
Overview
Salary
Demand
Core Tasks
Technology Skills
Tools Used
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Top 10 Skills
Top 10 Abilities
Top 10 Work Activities
Detailed Work Activities
Work Context
Education
Majors
Interests
Top 10 Work Styles
Work Values
Related Careers
Overview
Job Zone Four: Considerable Preparation Needed
Experience
A considerable amount of work-related skill, knowledge, or experience is needed for these occupations. For example, an accountant must complete four years of college and work for several years in accounting to be considered qualified.
Education
Most of these occupations require a four-year bachelor's degree, but some do not.
Job Training
Employees in these occupations usually need several years of work-related experience, on-the-job training, and/or vocational training.
Examples
Many of these occupations involve coordinating, supervising, managing, or training others. Examples include real estate brokers, sales managers, database administrators, graphic designers, chemists, art directors, and cost estimators.
Direct and coordinate activities of personnel engaged in preparation of radio or television station program schedules and programs, such as sports or news.
Salary Salary
Salary at 10th Percentile: $36K
Salary at 25th Percentile: $51K
Median Salary: $76K
Salary at 75th Percentile: $118K
Salary at 90th Percentile: $184K
Demand
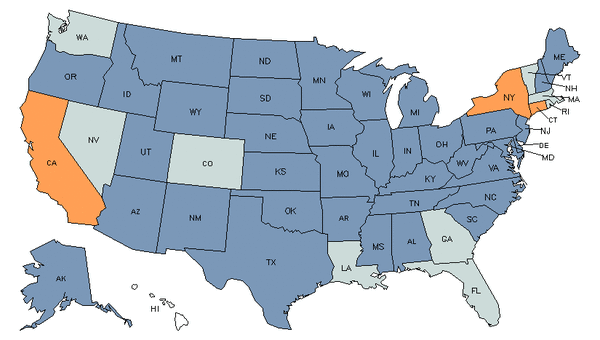

Core Tasks
Plan and schedule programming and event coverage, based on broadcast length, time availability, and other factors, such as community needs, ratings data, and viewer demographics.
Coordinate activities between departments, such as news and programming.
Direct and coordinate activities of personnel engaged in broadcast news, sports, or programming.
Monitor and review programming to ensure that schedules are met, guidelines are adhered to, and performances are of adequate quality.
Check completed program logs for accuracy and conformance with Federal Communications Commission (FCC) rules and regulations and resolve program log inaccuracies.
Establish work schedules and assign work to staff members.
Operate and maintain on-air and production audio equipment.
Monitor network transmissions for advisories concerning daily program schedules, program content, special feeds, or program changes.
Prepare copy and edit tape so that material is ready for broadcasting.
Confer with directors and production staff to discuss issues, such as production and casting problems, budgets, policies, and news coverage.
Develop budgets for programming and broadcasting activities and monitor expenditures to ensure that they remain within budgetary limits.
Develop ideas for programs and features that a station could produce.
Develop promotions for current programs and specials.
Evaluate new and existing programming to assess suitability and the need for changes, using information such as audience surveys and feedback.
Perform personnel duties, such as hiring staff and evaluating work performance.
Read news, read or record public service and promotional announcements, or perform other on-air duties.
Act as a liaison between talent and directors, providing information that performers or guests need to prepare for appearances and communicating relevant information from guests, performers, or staff to directors.
Review information about programs and schedules to ensure accuracy and provide such information to local media outlets.
Select, acquire, and maintain programs, music, films, and other needed materials and obtain legal clearances for their use as necessary.
Direct setup of remote facilities and install or cancel programs at remote stations.
Conduct interviews for broadcasts.
Cue announcers, actors, performers, and guests.
Participate in the planning and execution of fundraising activities.
Technology Skills
Technology
Example
Hot Technology
Tools Used
Tool
Example
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Communications and Media
89%
Knowledge of media production, communication, and dissemination techniques and methods. This includes alternative ways to inform and entertain via written, oral, and visual media.
English Language
87%
Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, rules of composition, and grammar.
Customer and Personal Service
81%
Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Administration and Management
80%
Knowledge of business and management principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people and resources.
Personnel and Human Resources
77%
Knowledge of principles and procedures for personnel recruitment, selection, training, compensation and benefits, labor relations and negotiation, and personnel information systems.
Computers and Electronics
76%
Knowledge of circuit boards, processors, chips, electronic equipment, and computer hardware and software, including applications and programming.
Telecommunications
76%
Knowledge of transmission, broadcasting, switching, control, and operation of telecommunications systems.
Clerical
71%
Knowledge of administrative and clerical procedures and systems such as word processing, managing files and records, stenography and transcription, designing forms, and other office procedures and terminology.
Education and Training
65%
Knowledge of principles and methods for curriculum and training design, teaching and instruction for individuals and groups, and the measurement of training effects.
Law and Government
64%
Knowledge of laws, legal codes, court procedures, precedents, government regulations, executive orders, agency rules, and the democratic political process.
Top 10 Skills
Critical Thinking
85%
Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Judgment and Decision Making
83%
Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Reading Comprehension
83%
Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Speaking
83%
Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Active Learning
80%
Understanding the implications of new information for both current and future problem-solving and decision-making.
Active Listening
80%
Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Coordination
80%
Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions.
Management of Personnel Resources
80%
Motivating, developing, and directing people as they work, identifying the best people for the job.
Time Management
80%
Managing one's own time and the time of others.
Complex Problem Solving
78%
Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Top 10 Abilities
Oral Comprehension
88%
The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
Written Comprehension
85%
The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
Oral Expression
83%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
Problem Sensitivity
83%
The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem.
Speech Clarity
80%
The ability to speak clearly so others can understand you.
Written Expression
80%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in writing so others will understand.
Deductive Reasoning
78%
The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
Inductive Reasoning
78%
The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events).
Information Ordering
78%
The ability to arrange things or actions in a certain order or pattern according to a specific rule or set of rules (e.g., patterns of numbers, letters, words, pictures, mathematical operations).
Originality
78%
The ability to come up with unusual or clever ideas about a given topic or situation, or to develop creative ways to solve a problem.
Top 10 Work Activities
Interacting With Computers
98%
Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
Communicating with Persons Outside Organization
95%
Communicating with people outside the organization, representing the organization to customers, the public, government, and other external sources. This information can be exchanged in person, in writing, or by telephone or e-mail.
Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates
95%
Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person.
Organizing, Planning, and Prioritizing Work
94%
Developing specific goals and plans to prioritize, organize, and accomplish your work.
Getting Information
93%
Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
Thinking Creatively
93%
Developing, designing, or creating new applications, ideas, relationships, systems, or products, including artistic contributions.
Updating and Using Relevant Knowledge
93%
Keeping up-to-date technically and applying new knowledge to your job.
Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events
91%
Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
Making Decisions and Solving Problems
90%
Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
Scheduling Work and Activities
90%
Scheduling events, programs, and activities, as well as the work of others.
Detailed Work Activities
Determine presentation subjects or content.
Manage content of broadcasts or presentations.
Coordinate reporting or editing activities.
Maintain logs of production activities.
Manage operations of artistic or entertainment departments or organizations.
Select staff, team members, or performers.
Discuss production content and progress with others.
Select materials or props.
Maintain inventories of materials, equipment, or products.
Develop promotional strategies or plans.
Edit audio or video recordings.
Direct fundraising or financing activities.
Verify accuracy of data.
Report news to the public.
Operate communications, transmissions, or broadcasting equipment.
Maintain recording or broadcasting equipment.
Direct productions or performances.
Interview others for news or entertainment purposes.
Coordinate logistics for productions or events.
Work Context
Electronic Mail
How often do you use electronic mail in this job?
Telephone
How often do you have telephone conversations in this job?
Indoors, Environmentally Controlled
How often does this job require working indoors in environmentally controlled conditions?
Contact With Others
How much does this job require the worker to be in contact with others (face-to-face, by telephone, or otherwise) in order to perform it?
Deal With External Customers
How important is it to work with external customers or the public in this job?
Face-to-Face Discussions
How often do you have to have face-to-face discussions with individuals or teams in this job?
Work With Work Group or Team
How important is it to work with others in a group or team in this job?
Time Pressure
How often does this job require the worker to meet strict deadlines?
Frequency of Decision Making
How frequently is the worker required to make decisions that affect other people, the financial resources, and/or the image and reputation of the organization?
Freedom to Make Decisions
How much decision making freedom, without supervision, does the job offer?
Education
Majors based on the broader career Producers and Directors
Major
Interests
Enterprising
100%
Enterprising occupations frequently involve starting up and carrying out projects. These occupations can involve leading people and making many decisions. Sometimes they require risk taking and often deal with business.
Conventional
72%
Conventional occupations frequently involve following set procedures and routines. These occupations can include working with data and details more than with ideas. Usually there is a clear line of authority to follow.
Artistic
62%
Artistic occupations frequently involve working with forms, designs and patterns. They often require self-expression and the work can be done without following a clear set of rules.
Social
39%
Social occupations frequently involve working with, communicating with, and teaching people. These occupations often involve helping or providing service to others.
Investigative
24%
Investigative occupations frequently involve working with ideas, and require an extensive amount of thinking. These occupations can involve searching for facts and figuring out problems mentally.
Realistic
19%
Realistic occupations frequently involve work activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions. They often deal with plants, animals, and real-world materials like wood, tools, and machinery. Many of the occupations require working outside, and do not involve a lot of paperwork or working closely with others.
Top 10 Work Styles
Attention to Detail
92%
Job requires being careful about detail and thorough in completing work tasks.
Dependability
92%
Job requires being reliable, responsible, and dependable, and fulfilling obligations.
Cooperation
90%
Job requires being pleasant with others on the job and displaying a good-natured, cooperative attitude.
Self Control
90%
Job requires maintaining composure, keeping emotions in check, controlling anger, and avoiding aggressive behavior, even in very difficult situations.
Adaptability/Flexibility
88%
Job requires being open to change (positive or negative) and to considerable variety in the workplace.
Analytical Thinking
88%
Job requires analyzing information and using logic to address work-related issues and problems.
Innovation
88%
Job requires creativity and alternative thinking to develop new ideas for and answers to work-related problems.
Integrity
88%
Job requires being honest and ethical.
Social Orientation
88%
Job requires preferring to work with others rather than alone, and being personally connected with others on the job.
Stress Tolerance
88%
Job requires accepting criticism and dealing calmly and effectively with high stress situations.
Work Values
Achievement
86%
Occupations that satisfy this work value are results oriented and allow employees to use their strongest abilities, giving them a feeling of accomplishment. Corresponding needs are Ability Utilization and Achievement.
Independence
86%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to work on their own and make decisions. Corresponding needs are Creativity, Responsibility and Autonomy.
Recognition
86%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer advancement, potential for leadership, and are often considered prestigious. Corresponding needs are Advancement, Authority, Recognition and Social Status.
Working Conditions
77%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer job security and good working conditions. Corresponding needs are Activity, Compensation, Independence, Security, Variety and Working Conditions.
Relationships
72%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to provide service to others and work with co-workers in a friendly non-competitive environment. Corresponding needs are Co-workers, Moral Values and Social Service.
Support
53%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer supportive management that stands behind employees. Corresponding needs are Company Policies, Supervision: Human Relations and Supervision: Technical.
