Quality Control Systems Managers
Overview
SaveJob Zone Four: Considerable Preparation Needed
Experience
A considerable amount of work-related skill, knowledge, or experience is needed for these occupations. For example, an accountant must complete four years of college and work for several years in accounting to be considered qualified.
Education
Most of these occupations require a four-year bachelor's degree, but some do not.
Job Training
Employees in these occupations usually need several years of work-related experience, on-the-job training, and/or vocational training.
Examples
Many of these occupations involve coordinating, supervising, managing, or training others. Examples include real estate brokers, sales managers, database administrators, graphic designers, conservation scientists, art directors, and cost estimators.
Plan, direct, or coordinate quality assurance programs. Formulate quality control policies and control quality of laboratory and production efforts.
Yearly Salary
| High: | $181K |
| Median: | $108K |
| Low: | $67K |
Demand
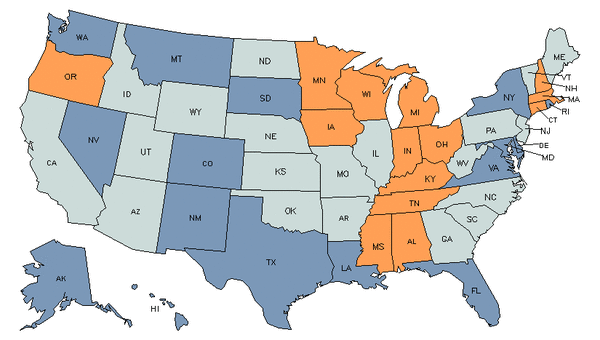

Core Tasks
- Stop production if serious product defects are present.
- Monitor performance of quality control systems to ensure effectiveness and efficiency.
- Review and update standard operating procedures or quality assurance manuals.
- Analyze quality control test results and provide feedback and interpretation to production management or staff.
- Review quality documentation necessary for regulatory submissions and inspections.
- Verify that raw materials, purchased parts or components, in-process samples, and finished products meet established testing and inspection standards.
- Direct product testing activities throughout production cycles.
- Oversee workers including supervisors, inspectors, or laboratory workers engaged in testing activities.
- Instruct staff in quality control and analytical procedures.
- Direct the tracking of defects, test results, or other regularly reported quality control data.
- Participate in the development of product specifications.
- Collect and analyze production samples to evaluate quality.
- Identify quality problems or areas for improvement and recommend solutions.
- Communicate quality control information to all relevant organizational departments, outside vendors, or contractors.
- Produce reports regarding nonconformance of products or processes, daily production quality, root cause analyses, or quality trends.
- Identify critical points in the manufacturing process and specify sampling procedures to be used at these points.
- Monitor development of new products to help identify possible problems for mass production.
- Create and implement inspection and testing criteria or procedures.
- Document testing procedures, methodologies, or criteria.
- Coordinate the selection and implementation of quality control equipment, such as inspection gauges.
- Review statistical studies, technological advances, or regulatory standards and trends to stay abreast of issues in the field of quality control.
- Generate and maintain quality control operating budgets.
- Instruct vendors or contractors on quality guidelines, testing procedures, or ways to eliminate deficiencies.
- Audit and inspect subcontractor facilities including external laboratories.
- Confer with marketing and sales departments to define client requirements and expectations.
- Evaluate new testing and sampling methodologies or technologies to determine usefulness.
- Review and approve quality plans submitted by contractors.
Technology Skills
Technology
Example
Hot Technology
Tools Used
Tool
Example
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Production and Processing
83%
Knowledge of raw materials, production processes, quality control, costs, and other techniques for maximizing the effective manufacture and distribution of goods.
Education and Training
82%
Knowledge of principles and methods for curriculum and training design, teaching and instruction for individuals and groups, and the measurement of training effects.
English Language
82%
Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, and rules of composition and grammar.
Chemistry
78%
Knowledge of the chemical composition, structure, and properties of substances and of the chemical processes and transformations that they undergo. This includes uses of chemicals and their interactions, danger signs, production techniques, and disposal methods.
Customer and Personal Service
76%
Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Administration and Management
75%
Knowledge of business and management principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people and resources.
Mathematics
72%
Knowledge of arithmetic, algebra, geometry, calculus, statistics, and their applications.
Engineering and Technology
71%
Knowledge of the practical application of engineering science and technology. This includes applying principles, techniques, procedures, and equipment to the design and production of various goods and services.
Public Safety and Security
70%
Knowledge of relevant equipment, policies, procedures, and strategies to promote effective local, state, or national security operations for the protection of people, data, property, and institutions.
Computers and Electronics
67%
Knowledge of circuit boards, processors, chips, electronic equipment, and computer hardware and software, including applications and programming.
Top 10 Skills
Judgment and Decision Making
80%
Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Quality Control Analysis
80%
Conducting tests and inspections of products, services, or processes to evaluate quality or performance.
Reading Comprehension
80%
Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work-related documents.
Active Listening
78%
Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Monitoring
78%
Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
Speaking
78%
Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Writing
78%
Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Complex Problem Solving
75%
Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Coordination
75%
Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions.
Critical Thinking
75%
Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions, or approaches to problems.
Top 10 Abilities
Problem Sensitivity
83%
The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing that there is a problem.
Deductive Reasoning
80%
The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
Inductive Reasoning
80%
The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events).
Near Vision
80%
The ability to see details at close range (within a few feet of the observer).
Oral Comprehension
80%
The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
Oral Expression
80%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
Written Comprehension
80%
The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
Written Expression
80%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in writing so others will understand.
Speech Clarity
75%
The ability to speak clearly so others can understand you.
Flexibility of Closure
70%
The ability to identify or detect a known pattern (a figure, object, word, or sound) that is hidden in other distracting material.
Top 10 Work Activities
Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates
96%
Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person.
Documenting/Recording Information
96%
Entering, transcribing, recording, storing, or maintaining information in written or electronic/magnetic form.
Analyzing Data or Information
93%
Identifying the underlying principles, reasons, or facts of information by breaking down information or data into separate parts.
Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events
93%
Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
Working with Computers
92%
Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
Evaluating Information to Determine Compliance with Standards
91%
Using relevant information and individual judgment to determine whether events or processes comply with laws, regulations, or standards.
Getting Information
88%
Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
Making Decisions and Solving Problems
86%
Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
Organizing, Planning, and Prioritizing Work
86%
Developing specific goals and plans to prioritize, organize, and accomplish your work.
Monitoring Processes, Materials, or Surroundings
85%
Monitoring and reviewing information from materials, events, or the environment, to detect or assess problems.
Detailed Work Activities
- Inspect condition or functioning of facilities or equipment.
- Direct operational or production activities.
- Document organizational or operational procedures.
- Monitor organizational procedures to ensure proper functioning.
- Review documents or materials for compliance with policies or regulations.
- Analyze data to inform operational decisions or activities.
- Confer with organizational members to accomplish work activities.
- Evaluate quality of materials or products.
- Supervise employees.
- Manage control system activities in organizations.
- Conduct employee training programs.
- Direct organizational operations, projects, or services.
- Develop specifications for new products or processes.
- Analyze data to assess operational or project effectiveness.
- Recommend organizational process or policy changes.
- Prepare operational progress or status reports.
- Communicate organizational policies and procedures.
- Communicate organizational information to customers or other stakeholders.
- Monitor facilities or operational systems.
- Develop organizational methods or procedures.
- Implement organizational process or policy changes.
- Develop operating strategies, plans, or procedures.
- Maintain knowledge of current developments in area of expertise.
- Prepare operational budgets.
- Advise customers on technical or procedural issues.
- Evaluate new technologies or methods.
- Review details of technical drawings or specifications.
Education
Interests
Conventional
82%
Work involves following procedures and regulations to organize information or data, typically in a business setting. Conventional occupations are often associated with office work, accounting, mathematics/statistics, information technology, finance, or human resources.
Enterprising
73%
Work involves managing, negotiating, marketing, or selling, typically in a business setting, or leading or advising people in political and legal situations. Enterprising occupations are often associated with business initiatives, sales, marketing/advertising, finance, management/administration, professional advising, public speaking, politics, or law.
Investigative
58%
Work involves studying and researching non-living objects, living organisms, disease or other forms of impairment, or human behavior. Investigative occupations are often associated with physical, life, medical, or social sciences, and can be found in the fields of humanities, mathematics/statistics, information technology, or health care service.
Realistic
52%
Work involves designing, building, or repairing of equipment, materials, or structures, engaging in physical activity, or working outdoors. Realistic occupations are often associated with engineering, mechanics and electronics, construction, woodworking, transportation, machine operation, agriculture, animal services, physical or manual labor, athletics, or protective services.
Social
30%
Work involves helping, teaching, advising, assisting, or providing service to others. Social occupations are often associated with social, health care, personal service, teaching/education, or religious activities.
Artistic
17%
Work involves creating original visual artwork, performances, written works, food, or music for a variety of media, or applying artistic principles to the design of various objects and materials. Artistic occupations are often associated with visual arts, applied arts and design, performing arts, music, creative writing, media, or culinary art.
Work Values
Support
77%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer supportive management that stands behind employees. Corresponding needs are Company Policies, Supervision: Human Relations and Supervision: Technical.
Achievement
72%
Occupations that satisfy this work value are results oriented and allow employees to use their strongest abilities, giving them a feeling of accomplishment. Corresponding needs are Ability Utilization and Achievement.
Independence
72%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to work on their own and make decisions. Corresponding needs are Creativity, Responsibility and Autonomy.
Recognition
67%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer advancement, potential for leadership, and are often considered prestigious. Corresponding needs are Advancement, Authority, Recognition and Social Status.
Working Conditions
65%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer job security and good working conditions. Corresponding needs are Activity, Compensation, Independence, Security, Variety and Working Conditions.
Relationships
58%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to provide service to others and work with co-workers in a friendly non-competitive environment. Corresponding needs are Co-workers, Moral Values and Social Service.
