Interviewers, Except Eligibility and Loan
Overview
SaveJob Zone Three: Medium Preparation Needed
Experience
Previous work-related skill, knowledge, or experience is required for these occupations. For example, an electrician must have completed three or four years of apprenticeship or several years of vocational training, and often must have passed a licensing exam, in order to perform the job.
Education
Most occupations in this zone require training in vocational schools, related on-the-job experience, or an associate's degree.
Job Training
Employees in these occupations usually need one or two years of training involving both on-the-job experience and informal training with experienced workers. A recognized apprenticeship program may be associated with these occupations.
Examples
These occupations usually involve using communication and organizational skills to coordinate, supervise, manage, or train others to accomplish goals. Examples include hydroelectric production managers, desktop publishers, electricians, agricultural technicians, barbers, court reporters and simultaneous captioners, and medical assistants.
Interview persons by telephone, mail, in person, or by other means for the purpose of completing forms, applications, or questionnaires. Ask specific questions, record answers, and assist persons with completing form. May sort, classify, and file forms.
Yearly Salary
| High: | $52K |
| Median: | $36K |
| Low: | $24K |
Demand
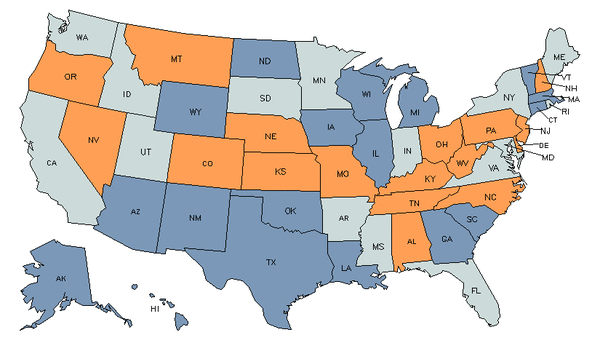

Core Tasks
- Ask questions in accordance with instructions to obtain various specified information, such as person's name, address, age, religious preference, or state of residency.
- Ensure payment for services by verifying benefits with the person's insurance provider or working out financing options.
- Identify and report problems in obtaining valid data.
- Locate and list addresses and households.
- Perform office duties, such as telemarketing or customer service inquiries, maintaining staff records, billing patients, or receiving payments.
- Review data obtained from interview for completeness and accuracy.
- Compile, record, and code results or data from interview or survey, using computer or specified form.
- Perform patient services, such as answering the telephone or assisting patients with financial or medical questions.
- Assist individuals in filling out applications or questionnaires.
- Identify and resolve inconsistencies in interviewees' responses by means of appropriate questioning or explanation.
- Contact individuals to be interviewed at home, place of business, or field location, by telephone, mail, or in person.
- Supervise or train other staff members.
- Collect and analyze data, such as studying old records, tallying the number of outpatients entering each day or week, or participating in federal, state, or local population surveys as a Census Enumerator.
- Prepare reports to provide answers in response to specific problems.
- Explain survey objectives and procedures to interviewees and interpret survey questions to help interviewees' comprehension.
- Meet with supervisor daily to submit completed assignments and discuss progress.
Technology Skills
Technology
Example
Hot Technology
Tools Used
Tool
Example
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Customer and Personal Service
90%
Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
English Language
75%
Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, and rules of composition and grammar.
Administrative
74%
Knowledge of administrative and office procedures and systems such as word processing, managing files and records, stenography and transcription, designing forms, and workplace terminology.
Computers and Electronics
70%
Knowledge of circuit boards, processors, chips, electronic equipment, and computer hardware and software, including applications and programming.
Mathematics
66%
Knowledge of arithmetic, algebra, geometry, calculus, statistics, and their applications.
Administration and Management
62%
Knowledge of business and management principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people and resources.
Communications and Media
54%
Knowledge of media production, communication, and dissemination techniques and methods. This includes alternative ways to inform and entertain via written, oral, and visual media.
Personnel and Human Resources
51%
Knowledge of principles and procedures for personnel recruitment, selection, training, compensation and benefits, labor relations and negotiation, and personnel information systems.
Therapy and Counseling
51%
Knowledge of principles, methods, and procedures for diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of physical and mental dysfunctions, and for career counseling and guidance.
Law and Government
50%
Knowledge of laws, legal codes, court procedures, precedents, government regulations, executive orders, agency rules, and the democratic political process.
Top 10 Skills
Active Listening
80%
Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Speaking
78%
Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Reading Comprehension
70%
Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work-related documents.
Social Perceptiveness
68%
Being aware of others' reactions and understanding why they react as they do.
Critical Thinking
65%
Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions, or approaches to problems.
Service Orientation
65%
Actively looking for ways to help people.
Time Management
65%
Managing one's own time and the time of others.
Writing
65%
Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Complex Problem Solving
63%
Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Coordination
60%
Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions.
Top 10 Abilities
Oral Expression
80%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
Oral Comprehension
78%
The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
Speech Clarity
78%
The ability to speak clearly so others can understand you.
Speech Recognition
78%
The ability to identify and understand the speech of another person.
Written Comprehension
70%
The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
Information Ordering
68%
The ability to arrange things or actions in a certain order or pattern according to a specific rule or set of rules (e.g., patterns of numbers, letters, words, pictures, mathematical operations).
Near Vision
68%
The ability to see details at close range (within a few feet of the observer).
Written Expression
68%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in writing so others will understand.
Deductive Reasoning
65%
The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
Inductive Reasoning
65%
The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events).
Top 10 Work Activities
Working with Computers
99%
Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates
93%
Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person.
Evaluating Information to Determine Compliance with Standards
90%
Using relevant information and individual judgment to determine whether events or processes comply with laws, regulations, or standards.
Documenting/Recording Information
88%
Entering, transcribing, recording, storing, or maintaining information in written or electronic/magnetic form.
Establishing and Maintaining Interpersonal Relationships
88%
Developing constructive and cooperative working relationships with others, and maintaining them over time.
Getting Information
88%
Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
Performing Administrative Activities
88%
Performing day-to-day administrative tasks such as maintaining information files and processing paperwork.
Making Decisions and Solving Problems
87%
Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
Organizing, Planning, and Prioritizing Work
87%
Developing specific goals and plans to prioritize, organize, and accomplish your work.
Processing Information
86%
Compiling, coding, categorizing, calculating, tabulating, auditing, or verifying information or data.
Detailed Work Activities
- Interview employees, customers, or others to collect information.
- Resolve operational performance problems.
- Verify accuracy of financial or transactional data.
- Negotiate financial arrangements.
- Collect deposits, payments or fees.
- Check data for recording errors.
- Compile data or documentation.
- Code data or other information.
- Answer telephones to direct calls or provide information.
- Assist individuals with paperwork.
- Supervise clerical or administrative personnel.
- Prepare research or technical reports.
- Confer with coworkers to coordinate work activities.
- Obtain personal or financial information about customers or applicants.
- Analyze operational or research data.
- Explain regulations, policies, or procedures.
Education
Interests
Conventional
86%
Work involves following procedures and regulations to organize information or data, typically in a business setting. Conventional occupations are often associated with office work, accounting, mathematics/statistics, information technology, finance, or human resources.
Social
59%
Work involves helping, teaching, advising, assisting, or providing service to others. Social occupations are often associated with social, health care, personal service, teaching/education, or religious activities.
Enterprising
53%
Work involves managing, negotiating, marketing, or selling, typically in a business setting, or leading or advising people in political and legal situations. Enterprising occupations are often associated with business initiatives, sales, marketing/advertising, finance, management/administration, professional advising, public speaking, politics, or law.
Investigative
28%
Work involves studying and researching non-living objects, living organisms, disease or other forms of impairment, or human behavior. Investigative occupations are often associated with physical, life, medical, or social sciences, and can be found in the fields of humanities, mathematics/statistics, information technology, or health care service.
Artistic
20%
Work involves creating original visual artwork, performances, written works, food, or music for a variety of media, or applying artistic principles to the design of various objects and materials. Artistic occupations are often associated with visual arts, applied arts and design, performing arts, music, creative writing, media, or culinary art.
Realistic
15%
Work involves designing, building, or repairing of equipment, materials, or structures, engaging in physical activity, or working outdoors. Realistic occupations are often associated with engineering, mechanics and electronics, construction, woodworking, transportation, machine operation, agriculture, animal services, physical or manual labor, athletics, or protective services.
Work Values
Relationships
81%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to provide service to others and work with co-workers in a friendly non-competitive environment. Corresponding needs are Co-workers, Moral Values and Social Service.
Support
72%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer supportive management that stands behind employees. Corresponding needs are Company Policies, Supervision: Human Relations and Supervision: Technical.
Independence
53%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to work on their own and make decisions. Corresponding needs are Creativity, Responsibility and Autonomy.
Working Conditions
53%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer job security and good working conditions. Corresponding needs are Activity, Compensation, Independence, Security, Variety and Working Conditions.
Achievement
34%
Occupations that satisfy this work value are results oriented and allow employees to use their strongest abilities, giving them a feeling of accomplishment. Corresponding needs are Ability Utilization and Achievement.
Recognition
29%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer advancement, potential for leadership, and are often considered prestigious. Corresponding needs are Advancement, Authority, Recognition and Social Status.
