Firefighters
Overview
Salary
Demand
Core Tasks
Technology Skills
Tools Used
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Top 10 Skills
Top 10 Abilities
Top 10 Work Activities
Detailed Work Activities
Majors
Interests
Top 10 Work Styles
Work Values
Related Careers
Overview
Job Zone Three: Medium Preparation Needed
Experience
Previous work-related skill, knowledge, or experience is required for these occupations. For example, an electrician must have completed three or four years of apprenticeship or several years of vocational training, and often must have passed a licensing exam, in order to perform the job.
Education
Most occupations in this zone require training in vocational schools, related on-the-job experience, or an associate's degree.
Job Training
Employees in these occupations usually need one or two years of training involving both on-the-job experience and informal training with experienced workers. A recognized apprenticeship program may be associated with these occupations.
Examples
These occupations usually involve using communication and organizational skills to coordinate, supervise, manage, or train others to accomplish goals. Examples include hydroelectric production managers, travel guides, electricians, agricultural technicians, barbers, court reporters, and medical assistants.
Control and extinguish fires or respond to emergency situations where life, property, or the environment is at risk. Duties may include fire prevention, emergency medical service, hazardous material response, search and rescue, and disaster assistance.
Salary Salary
Salary at 10th Percentile: $26K
Salary at 25th Percentile: $35K
Median Salary: $52K
Salary at 75th Percentile: $70K
Salary at 90th Percentile: $93K
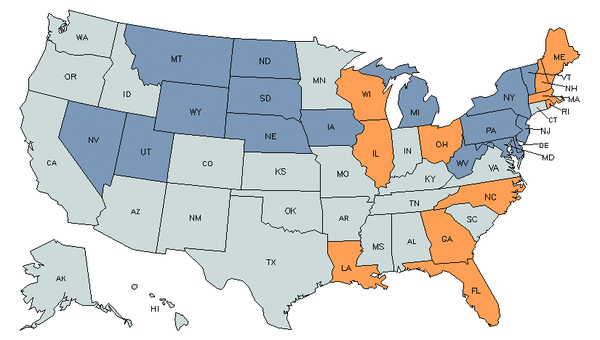
Demand

Core Tasks
Rescue victims from burning buildings, accident sites, and water hazards.
Dress with equipment such as fire-resistant clothing and breathing apparatus.
Assess fires and situations and report conditions to superiors to receive instructions, using two-way radios.
Move toward the source of a fire, using knowledge of types of fires, construction design, building materials, and physical layout of properties.
Respond to fire alarms and other calls for assistance, such as automobile and industrial accidents.
Create openings in buildings for ventilation or entrance, using axes, chisels, crowbars, electric saws, or core cutters.
Drive and operate fire fighting vehicles and equipment.
Inspect fire sites after flames have been extinguished to ensure that there is no further danger.
Position and climb ladders to gain access to upper levels of buildings, or to rescue individuals from burning structures.
Select and attach hose nozzles, depending on fire type, and direct streams of water or chemicals onto fires.
Collaborate with other firefighters as a member of a firefighting crew.
Maintain contact with fire dispatchers at all times to notify them of the need for additional firefighters and supplies, or to detail any difficulties encountered.
Collaborate with police to respond to accidents, disasters, and arson investigation calls.
Patrol burned areas after fires to locate and eliminate hot spots that may restart fires.
Maintain knowledge of current firefighting practices by participating in drills and by attending seminars, conventions, and conferences.
Participate in fire drills and demonstrations of fire fighting techniques.
Prepare written reports that detail specifics of fire incidents.
Inform and educate the public on fire prevention.
Participate in physical training activities to maintain a high level of physical fitness.
Protect property from water and smoke, using waterproof salvage covers, smoke ejectors, and deodorants.
Salvage property by removing broken glass, pumping out water, and ventilating buildings to remove smoke.
Clean and maintain fire stations and fire fighting equipment and apparatus.
Inspect buildings for fire hazards and compliance with fire prevention ordinances, testing and checking smoke alarms and fire suppression equipment as necessary.
Orient self in relation to fire, using compass and map, and collect supplies and equipment dropped by parachute.
Take action to contain any hazardous chemicals that could catch fire, leak, or spill.
Extinguish flames and embers to suppress fires, using shovels or engine- or hand-driven water or chemical pumps.
Technology Skills
Technology
Example
Hot Technology
Tools Used
Tool
Example
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Public Safety and Security
89%
Knowledge of relevant equipment, policies, procedures, and strategies to promote effective local, state, or national security operations for the protection of people, data, property, and institutions.
Building and Construction
84%
Knowledge of materials, methods, and the tools involved in the construction or repair of houses, buildings, or other structures such as highways and roads.
Customer and Personal Service
83%
Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Education and Training
76%
Knowledge of principles and methods for curriculum and training design, teaching and instruction for individuals and groups, and the measurement of training effects.
Mechanical
76%
Knowledge of machines and tools, including their designs, uses, repair, and maintenance.
Transportation
74%
Knowledge of principles and methods for moving people or goods by air, rail, sea, or road, including the relative costs and benefits.
English Language
72%
Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, rules of composition, and grammar.
Telecommunications
67%
Knowledge of transmission, broadcasting, switching, control, and operation of telecommunications systems.
Administration and Management
66%
Knowledge of business and management principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people and resources.
Chemistry
66%
Knowledge of the chemical composition, structure, and properties of substances and of the chemical processes and transformations that they undergo. This includes uses of chemicals and their interactions, danger signs, production techniques, and disposal methods.
Top 10 Skills
Active Listening
77%
Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Monitoring
77%
Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
Coordination
75%
Adjusting actions in relation to others' actions.
Operations Monitoring
75%
Watching gauges, dials, or other indicators to make sure a machine is working properly.
Critical Thinking
74%
Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Operation and Control
73%
Controlling operations of equipment or systems.
Service Orientation
72%
Actively looking for ways to help people.
Speaking
72%
Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Judgment and Decision Making
69%
Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Instructing
67%
Teaching others how to do something.
Top 10 Abilities
Problem Sensitivity
80%
The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem.
Static Strength
80%
The ability to exert maximum muscle force to lift, push, pull, or carry objects.
Multilimb Coordination
78%
The ability to coordinate two or more limbs (for example, two arms, two legs, or one leg and one arm) while sitting, standing, or lying down. It does not involve performing the activities while the whole body is in motion.
Oral Comprehension
78%
The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
Arm-Hand Steadiness
77%
The ability to keep your hand and arm steady while moving your arm or while holding your arm and hand in one position.
Oral Expression
77%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
Manual Dexterity
75%
The ability to quickly move your hand, your hand together with your arm, or your two hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble objects.
Reaction Time
75%
The ability to quickly respond (with the hand, finger, or foot) to a signal (sound, light, picture) when it appears.
Response Orientation
75%
The ability to choose quickly between two or more movements in response to two or more different signals (lights, sounds, pictures). It includes the speed with which the correct response is started with the hand, foot, or other body part.
Control Precision
74%
The ability to quickly and repeatedly adjust the controls of a machine or a vehicle to exact positions.
Top 10 Work Activities
Assisting and Caring for Others
88%
Providing personal assistance, medical attention, emotional support, or other personal care to others such as coworkers, customers, or patients.
Operating Vehicles, Mechanized Devices, or Equipment
88%
Running, maneuvering, navigating, or driving vehicles or mechanized equipment, such as forklifts, passenger vehicles, aircraft, or water craft.
Performing General Physical Activities
88%
Performing physical activities that require considerable use of your arms and legs and moving your whole body, such as climbing, lifting, balancing, walking, stooping, and handling of materials.
Inspecting Equipment, Structures, or Material
85%
Inspecting equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects.
Monitor Processes, Materials, or Surroundings
85%
Monitoring and reviewing information from materials, events, or the environment, to detect or assess problems.
Making Decisions and Solving Problems
84%
Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
Handling and Moving Objects
83%
Using hands and arms in handling, installing, positioning, and moving materials, and manipulating things.
Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates
82%
Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person.
Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events
82%
Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
Getting Information
80%
Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
Detailed Work Activities
Rescue people from hazardous situations.
Select tools, equipment, or technologies for use in operations or projects.
Assess characteristics of fires.
Relay information about incidents or emergencies to personnel using phones or two-way radios.
Locate fires or fire danger areas.
Respond to emergencies to provide assistance.
Operate firefighting equipment.
Examine debris to obtain information about causes of fires.
Prepare hoses or water supplies to fight fires.
Request emergency personnel.
Communicate with other workers to coordinate activities.
Patrol natural areas to ensure safety or enforce regulations.
Collaborate with law enforcement or security agencies to respond to incidents.
Demonstrate activity techniques or equipment use.
Attend training to learn new skills or update knowledge.
Maintain professional knowledge or certifications.
Prepare investigation or incident reports.
Participate in physical training to maintain fitness.
Protect property from fire or water damage.
Educate the public about fire safety or prevention.
Maintain fire fighting tools or equipment.
Inspect facilities to ensure compliance with fire regulations.
Inspect equipment to ensure safety or proper functioning.
Provide first aid or rescue assistance in emergencies.
Treat medical emergencies.
Implement advanced life support techniques.
Train personnel on proper operational procedures.
Majors
Major
Interests
Realistic
100%
Realistic occupations frequently involve work activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions. They often deal with plants, animals, and real-world materials like wood, tools, and machinery. Many of the occupations require working outside, and do not involve a lot of paperwork or working closely with others.
Social
69%
Social occupations frequently involve working with, communicating with, and teaching people. These occupations often involve helping or providing service to others.
Enterprising
48%
Enterprising occupations frequently involve starting up and carrying out projects. These occupations can involve leading people and making many decisions. Sometimes they require risk taking and often deal with business.
Investigative
43%
Investigative occupations frequently involve working with ideas, and require an extensive amount of thinking. These occupations can involve searching for facts and figuring out problems mentally.
Conventional
31%
Conventional occupations frequently involve following set procedures and routines. These occupations can include working with data and details more than with ideas. Usually there is a clear line of authority to follow.
Artistic
17%
Artistic occupations frequently involve working with forms, designs and patterns. They often require self-expression and the work can be done without following a clear set of rules.
Top 10 Work Styles
Dependability
94%
Job requires being reliable, responsible, and dependable, and fulfilling obligations.
Self Control
93%
Job requires maintaining composure, keeping emotions in check, controlling anger, and avoiding aggressive behavior, even in very difficult situations.
Stress Tolerance
93%
Job requires accepting criticism and dealing calmly and effectively with high stress situations.
Adaptability/Flexibility
92%
Job requires being open to change (positive or negative) and to considerable variety in the workplace.
Attention to Detail
91%
Job requires being careful about detail and thorough in completing work tasks.
Cooperation
90%
Job requires being pleasant with others on the job and displaying a good-natured, cooperative attitude.
Integrity
89%
Job requires being honest and ethical.
Leadership
89%
Job requires a willingness to lead, take charge, and offer opinions and direction.
Initiative
88%
Job requires a willingness to take on responsibilities and challenges.
Concern for Others
87%
Job requires being sensitive to others' needs and feelings and being understanding and helpful on the job.
Work Values
Support
84%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer supportive management that stands behind employees. Corresponding needs are Company Policies, Supervision: Human Relations and Supervision: Technical.
Relationships
81%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to provide service to others and work with co-workers in a friendly non-competitive environment. Corresponding needs are Co-workers, Moral Values and Social Service.
Achievement
79%
Occupations that satisfy this work value are results oriented and allow employees to use their strongest abilities, giving them a feeling of accomplishment. Corresponding needs are Ability Utilization and Achievement.
Recognition
69%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer advancement, potential for leadership, and are often considered prestigious. Corresponding needs are Advancement, Authority, Recognition and Social Status.
Independence
67%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to work on their own and make decisions. Corresponding needs are Creativity, Responsibility and Autonomy.
Working Conditions
65%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer job security and good working conditions. Corresponding needs are Activity, Compensation, Independence, Security, Variety and Working Conditions.
