Careers
>Transportation, Distribution & Logistics
>Facility and Mobile Equipment Maintenance
>Aircraft Mechanics and Service Technicians
Aircraft Mechanics and Service Technicians
Overview
Salary
Demand
Core Tasks
Technology Skills
Tools Used
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Top 10 Skills
Top 10 Abilities
Top 10 Work Activities
Detailed Work Activities
Work Context
Education
Majors
Interests
Top 10 Work Styles
Work Values
Related Careers
Overview
Job Zone Three: Medium Preparation Needed
Experience
Previous work-related skill, knowledge, or experience is required for these occupations. For example, an electrician must have completed three or four years of apprenticeship or several years of vocational training, and often must have passed a licensing exam, in order to perform the job.
Education
Most occupations in this zone require training in vocational schools, related on-the-job experience, or an associate's degree.
Job Training
Employees in these occupations usually need one or two years of training involving both on-the-job experience and informal training with experienced workers. A recognized apprenticeship program may be associated with these occupations.
Examples
These occupations usually involve using communication and organizational skills to coordinate, supervise, manage, or train others to accomplish goals. Examples include hydroelectric production managers, travel guides, electricians, agricultural technicians, barbers, court reporters, and medical assistants.
Diagnose, adjust, repair, or overhaul aircraft engines and assemblies, such as hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
Salary Salary
Salary at 10th Percentile: $38K
Salary at 25th Percentile: $51K
Median Salary: $66K
Salary at 75th Percentile: $85K
Salary at 90th Percentile: $103K
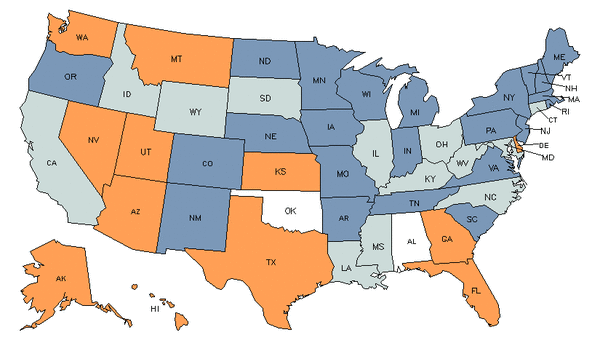
Demand

Core Tasks
Examine and inspect aircraft components, including landing gear, hydraulic systems, and deicers to locate cracks, breaks, leaks, or other problems.
Conduct routine and special inspections as required by regulations.
Inspect completed work to certify that maintenance meets standards and that aircraft are ready for operation.
Maintain repair logs, documenting all preventive and corrective aircraft maintenance.
Read and interpret maintenance manuals, service bulletins, and other specifications to determine the feasibility and method of repairing or replacing malfunctioning or damaged components.
Inspect airframes for wear or other defects.
Measure parts for wear, using precision instruments.
Modify aircraft structures, space vehicles, systems, or components, following drawings, schematics, charts, engineering orders, and technical publications.
Check for corrosion, distortion, and invisible cracks in the fuselage, wings, and tail, using x-ray and magnetic inspection equipment.
Examine engines through specially designed openings while working from ladders or scaffolds, or use hoists or lifts to remove the entire engine from an aircraft.
Obtain fuel and oil samples and check them for contamination.
Disassemble engines and inspect parts, such as turbine blades or cylinders, for corrosion, wear, warping, cracks, and leaks, using precision measuring instruments, x-rays, and magnetic inspection equipment.
Maintain, repair, and rebuild aircraft structures, functional components, and parts, such as wings and fuselage, rigging, hydraulic units, oxygen systems, fuel systems, electrical systems, gaskets, or seals.
Replace or repair worn, defective, or damaged components, using hand tools, gauges, and testing equipment.
Read and interpret pilots' descriptions of problems to diagnose causes.
Test operation of engines and other systems, using test equipment, such as ignition analyzers, compression checkers, distributor timers, or ammeters.
Measure the tension of control cables.
Spread plastic film over areas to be repaired to prevent damage to surrounding areas.
Assemble and install electrical, plumbing, mechanical, hydraulic, and structural components and accessories, using hand or power tools.
Remove or install aircraft engines, using hoists or forklift trucks.
Fabricate defective sections or parts, using metal fabricating machines, saws, brakes, shears, and grinders.
Locate and mark dimensions and reference lines on defective or replacement parts, using templates, scribes, compasses, and steel rules.
Clean, refuel, and change oil in line service aircraft.
Reassemble engines following repair or inspection and reinstall engines in aircraft.
Service and maintain aircraft and related apparatus by performing activities such as flushing crankcases, cleaning screens, and or moving parts.
Cure bonded structures, using portable or stationary curing equipment.
Listen to operating engines to detect and diagnose malfunctions, such as sticking or burned valves.
Trim and shape replacement body sections to specified sizes and fits and secure sections in place, using adhesives, hand tools, and power tools.
Accompany aircraft on flights to make in-flight adjustments and corrections.
Install and align repaired or replacement parts for subsequent riveting or welding, using clamps and wrenches.
Inventory and requisition or order supplies, parts, materials, and equipment.
Remove or cut out defective parts or drill holes to gain access to internal defects or damage, using drills and punches.
Clean engines, sediment bulk and screens, and carburetors, adjusting carburetor float levels.
Determine repair limits for engine hot section parts.
Clean, strip, prime, and sand structural surfaces and materials to prepare them for bonding.
Communicate with other workers to coordinate fitting and alignment of heavy parts, or to facilitate processing of repair parts.
Remove, inspect, repair, and install in-flight refueling stores and external fuel tanks.
Prepare and paint aircraft surfaces.
Technology Skills
Technology
Example
Hot Technology
Tools Used
Tool
Example
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Mechanical
95%
Knowledge of machines and tools, including their designs, uses, repair, and maintenance.
English Language
75%
Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, rules of composition, and grammar.
Engineering and Technology
68%
Knowledge of the practical application of engineering science and technology. This includes applying principles, techniques, procedures, and equipment to the design and production of various goods and services.
Customer and Personal Service
66%
Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Mathematics
64%
Knowledge of arithmetic, algebra, geometry, calculus, statistics, and their applications.
Public Safety and Security
63%
Knowledge of relevant equipment, policies, procedures, and strategies to promote effective local, state, or national security operations for the protection of people, data, property, and institutions.
Transportation
60%
Knowledge of principles and methods for moving people or goods by air, rail, sea, or road, including the relative costs and benefits.
Administration and Management
59%
Knowledge of business and management principles involved in strategic planning, resource allocation, human resources modeling, leadership technique, production methods, and coordination of people and resources.
Design
59%
Knowledge of design techniques, tools, and principles involved in production of precision technical plans, blueprints, drawings, and models.
Physics
59%
Knowledge and prediction of physical principles, laws, their interrelationships, and applications to understanding fluid, material, and atmospheric dynamics, and mechanical, electrical, atomic and sub- atomic structures and processes.
Top 10 Skills
Equipment Maintenance
85%
Performing routine maintenance on equipment and determining when and what kind of maintenance is needed.
Repairing
85%
Repairing machines or systems using the needed tools.
Operations Monitoring
83%
Watching gauges, dials, or other indicators to make sure a machine is working properly.
Troubleshooting
83%
Determining causes of operating errors and deciding what to do about it.
Complex Problem Solving
78%
Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Critical Thinking
78%
Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions or approaches to problems.
Quality Control Analysis
78%
Conducting tests and inspections of products, services, or processes to evaluate quality or performance.
Reading Comprehension
75%
Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work related documents.
Monitoring
68%
Monitoring/Assessing performance of yourself, other individuals, or organizations to make improvements or take corrective action.
Operation and Control
68%
Controlling operations of equipment or systems.
Top 10 Abilities
Control Precision
80%
The ability to quickly and repeatedly adjust the controls of a machine or a vehicle to exact positions.
Finger Dexterity
80%
The ability to make precisely coordinated movements of the fingers of one or both hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble very small objects.
Information Ordering
80%
The ability to arrange things or actions in a certain order or pattern according to a specific rule or set of rules (e.g., patterns of numbers, letters, words, pictures, mathematical operations).
Problem Sensitivity
80%
The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing there is a problem.
Written Comprehension
80%
The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
Arm-Hand Steadiness
78%
The ability to keep your hand and arm steady while moving your arm or while holding your arm and hand in one position.
Manual Dexterity
78%
The ability to quickly move your hand, your hand together with your arm, or your two hands to grasp, manipulate, or assemble objects.
Near Vision
78%
The ability to see details at close range (within a few feet of the observer).
Deductive Reasoning
73%
The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
Inductive Reasoning
73%
The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events).
Top 10 Work Activities
Getting Information
93%
Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
Documenting/Recording Information
92%
Entering, transcribing, recording, storing, or maintaining information in written or electronic/magnetic form.
Inspecting Equipment, Structures, or Material
91%
Inspecting equipment, structures, or materials to identify the cause of errors or other problems or defects.
Evaluating Information to Determine Compliance with Standards
90%
Using relevant information and individual judgment to determine whether events or processes comply with laws, regulations, or standards.
Repairing and Maintaining Mechanical Equipment
88%
Servicing, repairing, adjusting, and testing machines, devices, moving parts, and equipment that operate primarily on the basis of mechanical (not electronic) principles.
Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events
87%
Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
Monitor Processes, Materials, or Surroundings
87%
Monitoring and reviewing information from materials, events, or the environment, to detect or assess problems.
Communicating with Supervisors, Peers, or Subordinates
84%
Providing information to supervisors, co-workers, and subordinates by telephone, in written form, e-mail, or in person.
Making Decisions and Solving Problems
84%
Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
Updating and Using Relevant Knowledge
84%
Keeping up-to-date technically and applying new knowledge to your job.
Detailed Work Activities
Inspect mechanical components of vehicles to identify problems.
Inspect completed work to ensure proper functioning.
Read technical information needed to perform maintenance or repairs.
Interpret blueprints, specifications, or diagrams to inform installation, development or operation activities.
Maintain repair or maintenance records.
Inspect structural components of vehicles to identify problems.
Test fluids to identify contamination or other problems.
Repair worn, damaged, or defective mechanical parts.
Replace worn, damaged, or defective mechanical parts.
Read work orders or descriptions of problems to determine repairs or modifications needed.
Test mechanical equipment to ensure proper functioning.
Inspect mechanical equipment to locate damage, defects, or wear.
Apply protective coverings to objects or surfaces near work areas.
Move large objects using heavy equipment.
Assemble electrical components, subsystems, or systems.
Install electrical components, equipment, or systems.
Install piping for installation or maintenance activities.
Lay out work according to specifications.
Fabricate parts or components.
Reassemble equipment after repair.
Clean equipment, parts, or tools to repair or maintain them in good working order.
Lubricate equipment to allow proper functioning.
Service vehicles to maintain functionality.
Cut materials according to specifications or needs.
Troubleshoot equipment or systems operation problems.
Remove parts or components from equipment.
Drill holes in parts, equipment, or materials.
Install machine or equipment replacement parts.
Align equipment or machinery.
Maintain inventories of materials, equipment, or products.
Order materials, supplies, or equipment.
Communicate with coworkers to coordinate installations or repairs.
Operate cranes, hoists, or other moving or lifting equipment.
Disassemble equipment to inspect for deficiencies.
Operate heating or drying equipment.
Observe equipment in operation to detect potential problems.
Determine operational criteria or specifications.
Paint surfaces or equipment.
Work Context
Frequency of Decision Making
How frequently is the worker required to make decisions that affect other people, the financial resources, and/or the image and reputation of the organization?
Impact of Decisions on Co-workers or Company Results
What results do your decisions usually have on other people or the image or reputation or financial resources of your employer?
Indoors, Not Environmentally Controlled
How often does this job require working indoors in non-controlled environmental conditions (e.g., warehouse without heat)?
Consequence of Error
How serious would the result usually be if the worker made a mistake that was not readily correctable?
Importance of Being Exact or Accurate
How important is being very exact or highly accurate in performing this job?
Wear Common Protective or Safety Equipment such as Safety Shoes, Glasses, Gloves, Hearing Protection, Hard Hats, or Life Jackets
How much does this job require wearing common protective or safety equipment such as safety shoes, glasses, gloves, hard hats or life jackets?
Sounds, Noise Levels Are Distracting or Uncomfortable
How often does this job require working exposed to sounds and noise levels that are distracting or uncomfortable?
Extremely Bright or Inadequate Lighting
How often does this job require working in extremely bright or inadequate lighting conditions?
Time Pressure
How often does this job require the worker to meet strict deadlines?
Spend Time Using Your Hands to Handle, Control, or Feel Objects, Tools, or Controls
How much does this job require using your hands to handle, control, or feel objects, tools or controls?
Education
Majors
Major
Interests
Realistic
100%
Realistic occupations frequently involve work activities that include practical, hands-on problems and solutions. They often deal with plants, animals, and real-world materials like wood, tools, and machinery. Many of the occupations require working outside, and do not involve a lot of paperwork or working closely with others.
Conventional
67%
Conventional occupations frequently involve following set procedures and routines. These occupations can include working with data and details more than with ideas. Usually there is a clear line of authority to follow.
Investigative
53%
Investigative occupations frequently involve working with ideas, and require an extensive amount of thinking. These occupations can involve searching for facts and figuring out problems mentally.
Enterprising
29%
Enterprising occupations frequently involve starting up and carrying out projects. These occupations can involve leading people and making many decisions. Sometimes they require risk taking and often deal with business.
Artistic
19%
Artistic occupations frequently involve working with forms, designs and patterns. They often require self-expression and the work can be done without following a clear set of rules.
Social
15%
Social occupations frequently involve working with, communicating with, and teaching people. These occupations often involve helping or providing service to others.
Top 10 Work Styles
Attention to Detail
98%
Job requires being careful about detail and thorough in completing work tasks.
Integrity
97%
Job requires being honest and ethical.
Dependability
87%
Job requires being reliable, responsible, and dependable, and fulfilling obligations.
Persistence
86%
Job requires persistence in the face of obstacles.
Self Control
83%
Job requires maintaining composure, keeping emotions in check, controlling anger, and avoiding aggressive behavior, even in very difficult situations.
Adaptability/Flexibility
81%
Job requires being open to change (positive or negative) and to considerable variety in the workplace.
Initiative
81%
Job requires a willingness to take on responsibilities and challenges.
Achievement/Effort
79%
Job requires establishing and maintaining personally challenging achievement goals and exerting effort toward mastering tasks.
Independence
77%
Job requires developing one's own ways of doing things, guiding oneself with little or no supervision, and depending on oneself to get things done.
Leadership
77%
Job requires a willingness to lead, take charge, and offer opinions and direction.
Work Values
Support
86%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer supportive management that stands behind employees. Corresponding needs are Company Policies, Supervision: Human Relations and Supervision: Technical.
Working Conditions
67%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer job security and good working conditions. Corresponding needs are Activity, Compensation, Independence, Security, Variety and Working Conditions.
Relationships
62%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to provide service to others and work with co-workers in a friendly non-competitive environment. Corresponding needs are Co-workers, Moral Values and Social Service.
Achievement
58%
Occupations that satisfy this work value are results oriented and allow employees to use their strongest abilities, giving them a feeling of accomplishment. Corresponding needs are Ability Utilization and Achievement.
Independence
53%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to work on their own and make decisions. Corresponding needs are Creativity, Responsibility and Autonomy.
Recognition
48%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer advancement, potential for leadership, and are often considered prestigious. Corresponding needs are Advancement, Authority, Recognition and Social Status.
