Philosophy and Religion Teachers, Postsecondary
Overview
SaveJob Zone Five: Extensive Preparation Needed
Experience
Extensive skill, knowledge, and experience are needed for these occupations. Many require more than five years of experience. For example, surgeons must complete four years of college and an additional five to seven years of specialized medical training to be able to do their job.
Education
Most of these occupations require graduate school. For example, they may require a master's degree, and some require a Ph.D., M.D., or J.D. (law degree).
Job Training
Employees may need some on-the-job training, but most of these occupations assume that the person will already have the required skills, knowledge, work-related experience, and/or training.
Examples
These occupations often involve coordinating, training, supervising, or managing the activities of others to accomplish goals. Very advanced communication and organizational skills are required. Examples include pharmacists, lawyers, astronomers, biologists, clergy, physician assistants, and veterinarians.
Teach courses in philosophy, religion, and theology. Includes both teachers primarily engaged in teaching and those who do a combination of teaching and research.
Yearly Salary
| High: | $155K |
| Median: | $76K |
| Low: | $40K |
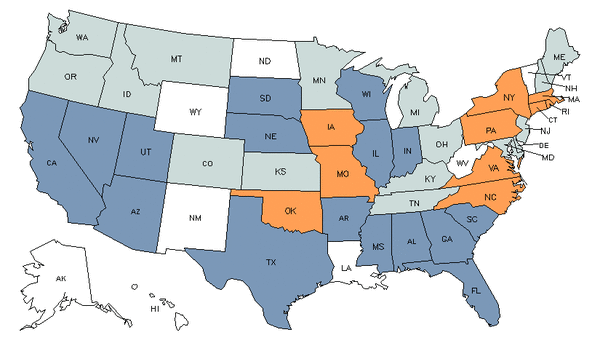
Demand

Core Tasks
- Evaluate and grade students' class work, assignments, and papers.
- Initiate, facilitate, and moderate classroom discussions.
- Prepare and deliver lectures to undergraduate or graduate students and the community on topics such as ethics, logic, and contemporary religious thought.
- Compile, administer, and grade examinations, or assign this work to others.
- Prepare course materials, such as syllabi, homework assignments, and handouts.
- Keep abreast of developments in the field by reading current literature, talking with colleagues, and participating in professional conferences.
- Maintain student attendance records, grades, and other required records.
- Perform administrative duties, such as serving as department head.
- Write articles and books.
- Conduct research in a particular field of knowledge and publish findings in professional journals, books, or electronic media.
- Maintain regularly scheduled office hours to advise and assist students.
- Plan, evaluate, and revise curricula, course content, course materials, and methods of instruction.
- Advise students on academic and vocational curricula and on career issues.
- Supervise undergraduate or graduate teaching, internship, and research work.
- Collaborate with colleagues to address teaching and research issues.
- Select and obtain materials and supplies, such as textbooks.
- Serve on academic or administrative committees that deal with institutional policies, departmental matters, and academic issues.
- Participate in student recruitment, registration, and placement activities.
- Compile bibliographies of specialized materials for outside reading assignments.
- Participate in campus and community events.
- Act as advisers to student organizations.
- Write grant proposals to procure external research funding.
Technology Skills
Technology
Example
Hot Technology
Tools Used
Tool
Example
Top 10 Knowledge Required
Philosophy and Theology
97%
Knowledge of different philosophical systems and religions. This includes their basic principles, values, ethics, ways of thinking, customs, practices, and their impact on human culture.
English Language
93%
Knowledge of the structure and content of the English language including the meaning and spelling of words, and rules of composition and grammar.
Education and Training
84%
Knowledge of principles and methods for curriculum and training design, teaching and instruction for individuals and groups, and the measurement of training effects.
History and Archeology
70%
Knowledge of historical events and their causes, indicators, and effects on civilizations and cultures.
Sociology and Anthropology
63%
Knowledge of group behavior and dynamics, societal trends and influences, human migrations, ethnicity, cultures, and their history and origins.
Law and Government
61%
Knowledge of laws, legal codes, court procedures, precedents, government regulations, executive orders, agency rules, and the democratic political process.
Communications and Media
59%
Knowledge of media production, communication, and dissemination techniques and methods. This includes alternative ways to inform and entertain via written, oral, and visual media.
Computers and Electronics
59%
Knowledge of circuit boards, processors, chips, electronic equipment, and computer hardware and software, including applications and programming.
Customer and Personal Service
59%
Knowledge of principles and processes for providing customer and personal services. This includes customer needs assessment, meeting quality standards for services, and evaluation of customer satisfaction.
Psychology
58%
Knowledge of human behavior and performance; individual differences in ability, personality, and interests; learning and motivation; psychological research methods; and the assessment and treatment of behavioral and affective disorders.
Top 10 Skills
Reading Comprehension
85%
Understanding written sentences and paragraphs in work-related documents.
Active Listening
83%
Giving full attention to what other people are saying, taking time to understand the points being made, asking questions as appropriate, and not interrupting at inappropriate times.
Instructing
83%
Teaching others how to do something.
Speaking
83%
Talking to others to convey information effectively.
Critical Thinking
80%
Using logic and reasoning to identify the strengths and weaknesses of alternative solutions, conclusions, or approaches to problems.
Writing
80%
Communicating effectively in writing as appropriate for the needs of the audience.
Learning Strategies
78%
Selecting and using training/instructional methods and procedures appropriate for the situation when learning or teaching new things.
Active Learning
75%
Understanding the implications of new information for both current and future problem-solving and decision-making.
Complex Problem Solving
70%
Identifying complex problems and reviewing related information to develop and evaluate options and implement solutions.
Judgment and Decision Making
68%
Considering the relative costs and benefits of potential actions to choose the most appropriate one.
Top 10 Abilities
Oral Expression
83%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in speaking so others will understand.
Speech Clarity
83%
The ability to speak clearly so others can understand you.
Written Comprehension
83%
The ability to read and understand information and ideas presented in writing.
Inductive Reasoning
80%
The ability to combine pieces of information to form general rules or conclusions (includes finding a relationship among seemingly unrelated events).
Oral Comprehension
80%
The ability to listen to and understand information and ideas presented through spoken words and sentences.
Written Expression
80%
The ability to communicate information and ideas in writing so others will understand.
Deductive Reasoning
78%
The ability to apply general rules to specific problems to produce answers that make sense.
Near Vision
70%
The ability to see details at close range (within a few feet of the observer).
Problem Sensitivity
65%
The ability to tell when something is wrong or is likely to go wrong. It does not involve solving the problem, only recognizing that there is a problem.
Speech Recognition
65%
The ability to identify and understand the speech of another person.
Top 10 Work Activities
Training and Teaching Others
96%
Identifying the educational needs of others, developing formal educational or training programs or classes, and teaching or instructing others.
Interpreting the Meaning of Information for Others
91%
Translating or explaining what information means and how it can be used.
Getting Information
90%
Observing, receiving, and otherwise obtaining information from all relevant sources.
Thinking Creatively
85%
Developing, designing, or creating new applications, ideas, relationships, systems, or products, including artistic contributions.
Making Decisions and Solving Problems
84%
Analyzing information and evaluating results to choose the best solution and solve problems.
Working with Computers
82%
Using computers and computer systems (including hardware and software) to program, write software, set up functions, enter data, or process information.
Updating and Using Relevant Knowledge
79%
Keeping up-to-date technically and applying new knowledge to your job.
Identifying Objects, Actions, and Events
77%
Identifying information by categorizing, estimating, recognizing differences or similarities, and detecting changes in circumstances or events.
Judging the Qualities of Objects, Services, or People
77%
Assessing the value, importance, or quality of things or people.
Establishing and Maintaining Interpersonal Relationships
76%
Developing constructive and cooperative working relationships with others, and maintaining them over time.
Detailed Work Activities
- Evaluate student work.
- Guide class discussions.
- Teach humanities courses at the college level.
- Administer tests to assess educational needs or progress.
- Prepare tests.
- Develop instructional materials.
- Stay informed about current developments in field of specialization.
- Attend training sessions or professional meetings to develop or maintain professional knowledge.
- Maintain student records.
- Write articles, books or other original materials in area of expertise.
- Direct department activities.
- Research topics in area of expertise.
- Evaluate effectiveness of educational programs.
- Develop instructional objectives.
- Advise students on academic or career matters.
- Supervise student research or internship work.
- Select educational materials or equipment.
- Order instructional or library materials or equipment.
- Serve on institutional or departmental committees.
- Promote educational institutions or programs.
- Perform student enrollment or registration activities.
- Compile specialized bibliographies or lists of materials.
- Plan community programs or activities for the general public.
- Write grant proposals.
Education
Interests
Social
100%
Work involves helping, teaching, advising, assisting, or providing service to others. Social occupations are often associated with social, health care, personal service, teaching/education, or religious activities.
Investigative
74%
Work involves studying and researching non-living objects, living organisms, disease or other forms of impairment, or human behavior. Investigative occupations are often associated with physical, life, medical, or social sciences, and can be found in the fields of humanities, mathematics/statistics, information technology, or health care service.
Artistic
54%
Work involves creating original visual artwork, performances, written works, food, or music for a variety of media, or applying artistic principles to the design of various objects and materials. Artistic occupations are often associated with visual arts, applied arts and design, performing arts, music, creative writing, media, or culinary art.
Conventional
47%
Work involves following procedures and regulations to organize information or data, typically in a business setting. Conventional occupations are often associated with office work, accounting, mathematics/statistics, information technology, finance, or human resources.
Enterprising
41%
Work involves managing, negotiating, marketing, or selling, typically in a business setting, or leading or advising people in political and legal situations. Enterprising occupations are often associated with business initiatives, sales, marketing/advertising, finance, management/administration, professional advising, public speaking, politics, or law.
Realistic
35%
Work involves designing, building, or repairing of equipment, materials, or structures, engaging in physical activity, or working outdoors. Realistic occupations are often associated with engineering, mechanics and electronics, construction, woodworking, transportation, machine operation, agriculture, animal services, physical or manual labor, athletics, or protective services.
Work Values
Achievement
81%
Occupations that satisfy this work value are results oriented and allow employees to use their strongest abilities, giving them a feeling of accomplishment. Corresponding needs are Ability Utilization and Achievement.
Independence
81%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to work on their own and make decisions. Corresponding needs are Creativity, Responsibility and Autonomy.
Recognition
77%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer advancement, potential for leadership, and are often considered prestigious. Corresponding needs are Advancement, Authority, Recognition and Social Status.
Relationships
77%
Occupations that satisfy this work value allow employees to provide service to others and work with co-workers in a friendly non-competitive environment. Corresponding needs are Co-workers, Moral Values and Social Service.
Working Conditions
69%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer job security and good working conditions. Corresponding needs are Activity, Compensation, Independence, Security, Variety and Working Conditions.
Support
34%
Occupations that satisfy this work value offer supportive management that stands behind employees. Corresponding needs are Company Policies, Supervision: Human Relations and Supervision: Technical.
